By Matthew Perrone
U.S. officials on Monday approved the first long-acting drug to protect babies and toddlers against a respiratory virus that sends tens of thousands of American children to the hospital each year.
RSV is a cold-like nuisance for most healthy people, but it can be life-threatening in the very young and the elderly.
The Food and Drug Administration approved the injection for infants and children up to 2 years old who face increased risk of severe RSV.
“Today’s approval addresses the great need for products to help reduce the impact of RSV disease on children, families and the health care system” said FDA's Dr. John Farley in a statement.
Last year, a surge in RSV cases flooded U.S. hospitals with wheezing children. There are no vaccines for babies yet, though Pfizer and other companies are working on them.
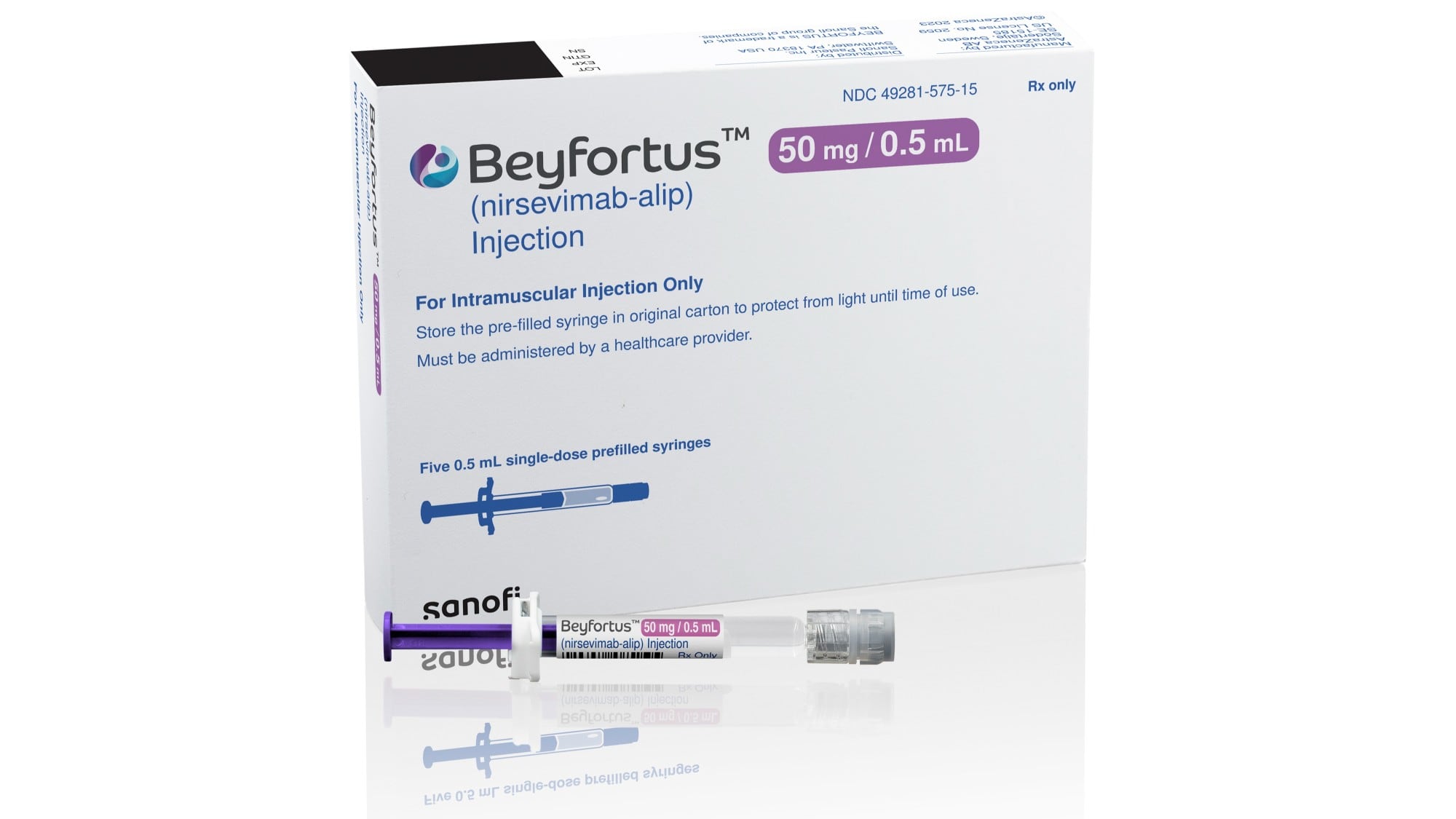
AstraZeneca’s drug, to be sold under the brand name Beyfortus, is a laboratory-made version of an antibody that helps the immune system fight off RSV. Under the FDA approval, babies — including preterm infants — can receive a single injection to protect against their first season of RSV, which typically lasts about five months. Children up to age 2 can receive another dose to protect them during their second season facing the virus.
Beyfortus, which will be marketed in the U.S. by Sanofi, is already approved in Canada, Europe and the U.K. Sanofi did not immediately announce the U.S. price of the treatment.
FDA officials approved the drug based on three studies showing Beyfortus reduced the risk of RSV infection between 70% and 75% among infants and children 2 and younger.
Advisers to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention will meet early next month to recommend exactly who should get the drug.
A similar antibody drug won FDA approval more than 20 years ago, but it’s only recommended for high-risk babies and requires monthly injections. Pediatricians say the drug is underutilized and they expect the longer-lasting effect of AstraZeneca's shot to improve uptake.
In the U.S., about 58,000 children younger than 5 are hospitalized for RSV each year and several hundred die.
After decades of setbacks for RSV research, drugmakers have made big strides this year, launching the first vaccines against the virus. In May, the FDA approved two RSV vaccines for older adults from GlaxoSmithKline and Pfizer. In August, the FDA is expected to make a decision on approving Pfizer’s vaccine for pregnant women, with the aim of passing along protection to their newborns.
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Science and Educational Media Group. The AP is solely responsible for all content.