By Michelle Liu and Mike Stobbe
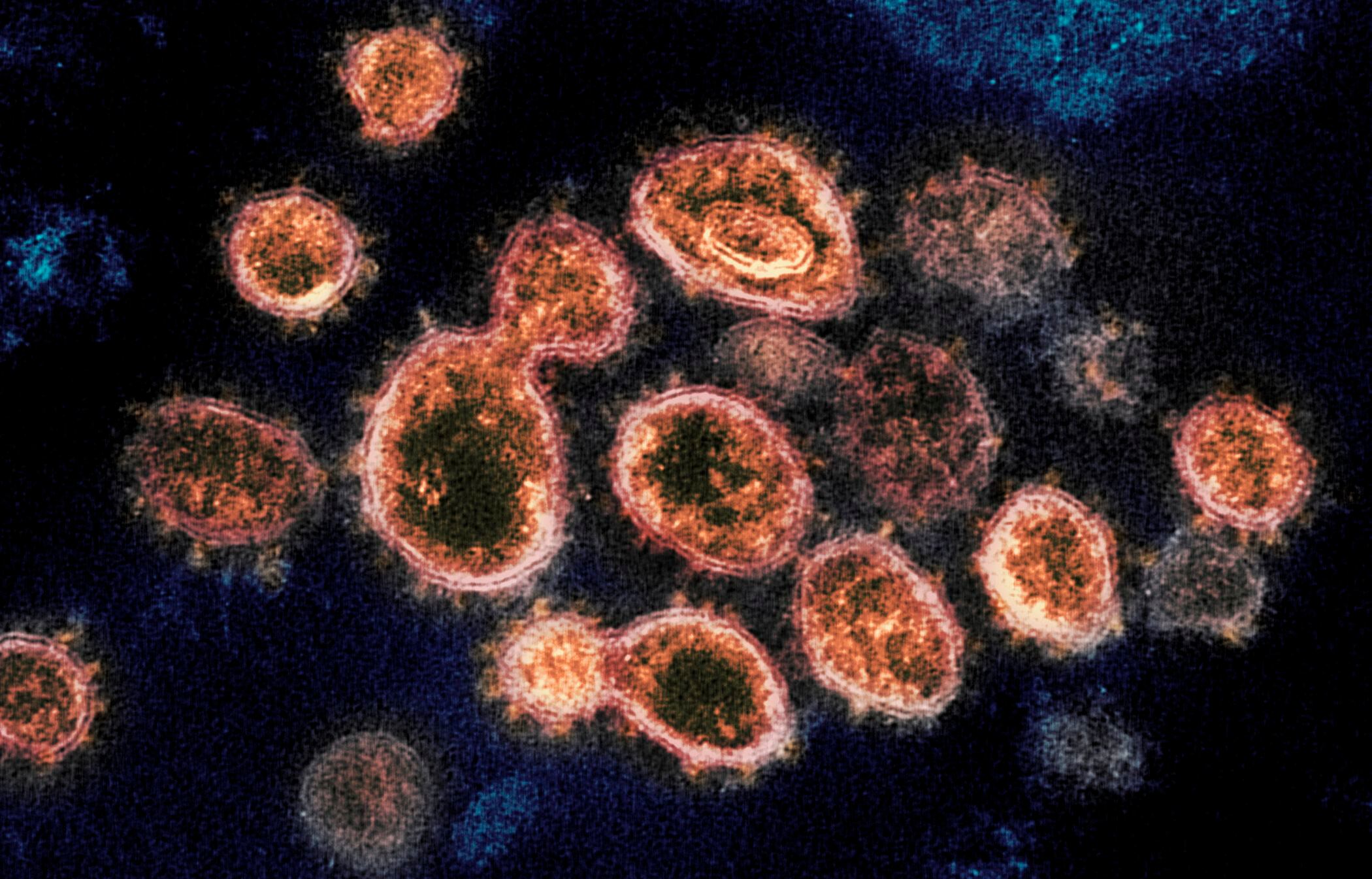
A new variant of the coronavirus emerged Thursday in the United States, posing yet another public health challenge in a country already losing more than 3,000 people to COVID-19 every day.
The mutated version of the virus, first identified in South Africa, was found in two cases in South Carolina. Public health officials said it’s almost certain that there are more infections that have not been identified yet. They are also concerned that this version spreads more easily and that vaccines could be less effective against it.
The two cases were discovered in adults in different regions of the state and do not appear to be connected. Neither of the people infected has traveled recently, the South Carolina Department of Health and Environmental Control said Thursday.
“That’s frightening,” because it means there could be more undetected cases within the state, said Dr. Krutika Kuppalli, an infectious diseases physician at the Medical University of South Carolina in Charleston. “It's probably more widespread.”
The arrival of the variant shows that "the fight against this deadly virus is far from over,” Dr. Brannon Traxler, South Carolina's interim public health director, said in a statement. “While more COVID-19 vaccines are on the way, supplies are still limited. Every one of us must recommit to the fight by recognizing that we are all on the front lines now. We are all in this together.”
Viruses constantly mutate, and coronavirus variants are circulating around the globe, but scientists are primarily concerned with the emergence of three that researchers believe may spread more easily. Other variants first reported in the United Kingdom and Brazil were previously confirmed in the U.S.
As the variants bring a potential for greater infection risks in the U.S., pandemic-weary lawmakers in several states are pushing back against mask mandates, business closures and other protective restrictions ordered by governors.
States including Arizona, Michigan, Ohio, Maryland, Kentucky and Indiana are weighing proposals to limit their governors' abilities to impose emergency restrictions. Wisconsin’s Republican-controlled Assembly had been expected to vote to repeal Democratic Gov. Tony Evers’ mask mandate, but lawmakers abruptly called off the vote Thursday in the face of broad criticism and out of concern it would jeopardize more than $49 million in federal aid. Pennsylvania lawmakers are considering a constitutional amendment to strip the governor of many of his emergency powers.
Governors argue that they need authority to act swiftly in a crisis, and limitations could slow critical emergency responses.
Meanwhile, Nebraska health officials said the state could be days away from lifting restrictions on indoor gatherings, citing a low percentage of COVID-19 hospitalizations. Other states seeing declining infections are also loosening limitations on restaurants and other businesses, though experts have warned the public to stay vigilant about masks and social distancing or risk further surges.
In South Carolina, the state health agency said the variant was found in one person from the state's coastal region and another in its northeastern corner. The state gave little other information, citing privacy concerns, though Traxler said neither of the people was contagious any longer.
“Both were tested very early in the month, and my understanding is that both are doing well,” Traxler said.
South Carolina Gov. Henry McMaster, a Republican, loosened most of the state’s remaining pandemic restrictions in the fall. Spokesman Brian Symmes said McMaster does not plan to order new restrictions based on the discovery of the variant.
“This is important information for South Carolinians to have," McMaster said in a tweet, “but it isn’t a reason for panic.”
Scientists last week reported preliminary signs that some of the recent mutations may modestly curb the effectiveness of two vaccines, although they stressed that the shots still protect against the disease. There are also signs that some of the new mutations may undermine tests for the virus and reduce the effectiveness of certain treatments.
The coronavirus has already sickened millions and killed roughly 430,000 people in the United States.
While the rollout of vaccines has been slow, President Joe Biden has pledged to deliver 100 million injections in his first 100 days in office — and suggested it's possible the U.S. could reach 1.5 million shots a day.
While some European countries do extensive genetic testing to detect these variants, the U.S. has done little of this detective work. But scientists have been been quickly trying to do more, which has revealed the more contagious variants.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has reported at least 315 cases of the U.K.-discovered variant in the United States. Those reports have come from at least 28 states, and health officials believe it could become the dominant strain in the U.S. by March. That variant has been reported in at least 70 countries.
The first U.S. case of the variant found in Brazil was announced earlier this week by health officials in Minnesota. It was a person who recently traveled to that South American nation. That version of the virus has popped up in more than a half-dozen countries.
The variant first found in South Africa was detected in October. Since then, it has been found in at least 30 other countries.
Some tests suggest the South African and Brazilian variants may be less susceptible to antibody drugs or antibody-rich blood from COVID-19 survivors, both of which help people fight off the virus.
Health officials also worry that if the virus changes enough, people might get COVID-19 a second time.
Biden on Monday reinstated COVID-19 travel restrictions on most non-U.S. travelers from Brazil, the U.K. and South Africa. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that Americans avoid travel.
___
Stobbe reported from New York.
___
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Department of Science Education. The AP is solely responsible for all content.